README.md 14 KB
learning-linux
This is the repository for the training Learning Linux
Instructor
Pierre-Yves Barriat
ACELI Training Sessions
What is UNIX ?
- Operating System > Windows 10 (Microsoft), MacOSX (Apple), Android (Google), etc
- UNIX is a (family of) Operating System
- Invented by AT&T Bell Labs in late 60's
- Currently there are different versions and variants of UNIX > Solaris, AIX, HP-UX, etc.
- UNIX is not free or Open Source: "GNU is Not UNIX"
What is Linux ?
- GNU (80's) is a free, open source version of the UNIX OS, but without the most important element: the kernel
- Linux kernel was developed in 1991 by Linus Torvalds, a Finnish graduate student
- The association GNU/Linux is an operating system (say just "Linux") and provides an alternative to commercial operating systems
- Linux exists without GNU (eg Android) : used to power a multitude of systems... from your phone to your smart fridge
What is a Linux distribution ?
Many versions of Linux
Red Hat, Debian, Suse, etc
But one common linux kernel: kernel is like an engine. A distribution is an actual car that hosts the engine
Distributions differ from
- the application/management layer
- GUI (Graphical User Interface = desktop environment)
- software packages
- help-desk, support, language
Why Linux ?
- Linux is free
- Linux is supported on older computers (perf & updates)
- Linux has many more free applications
Security: there are very few viruses for Linux
Privacy: most Linux distributions don't collect your data at all
Reliability: if you want to stop something, you really can
Updates: package manager
Customisation: you can make Linux look, feel and behave as you want it to
Command Line Interface: faster & efficient
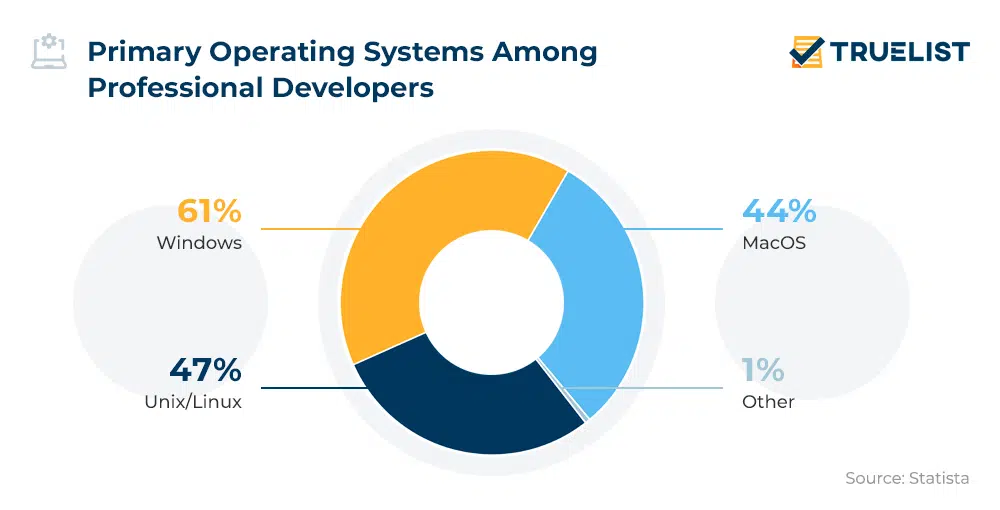
Linux Statistics
- 47% of professional developers use Linux-based operating systems (Statista)
- Linux powers 39.2% of websites whose operating system is known (W3Techs)
- Linux powers 85% of smartphones (Hayden James)
Why not Linux ?
- Hardware compatibility (printers, etc)
- Missing famous software (MS Office, Adobe, CAO, etc)
- Gaming
Workarounds
- Many devices "Linux compatible"
- Emulation (eg virtualbox), online usage, alternatives (GIMP)
- Difficult, but it exists emulation and Steam
Distribution: why Ubuntu ?
- easy to install and easy to use
- easy to maintain and update
- useful applications
- looks nice
- wide variety of supported applications
- strong community support
- better driver support
- LTS and staging releases available as per user needs
get the latest Ubuntu LTS : ubuntu-22.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso
Test Linux inside Windows: how ?
Using a virtual machine: test Linux without changing anything to your computer
You need to install a VM and then install the Linux inside
Get a Virtual Machine: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
VirtualBox + Extension Pack
Install Linux in a VM: Install Linux Inside Windows Using VirtualBox
Step by Step Guide
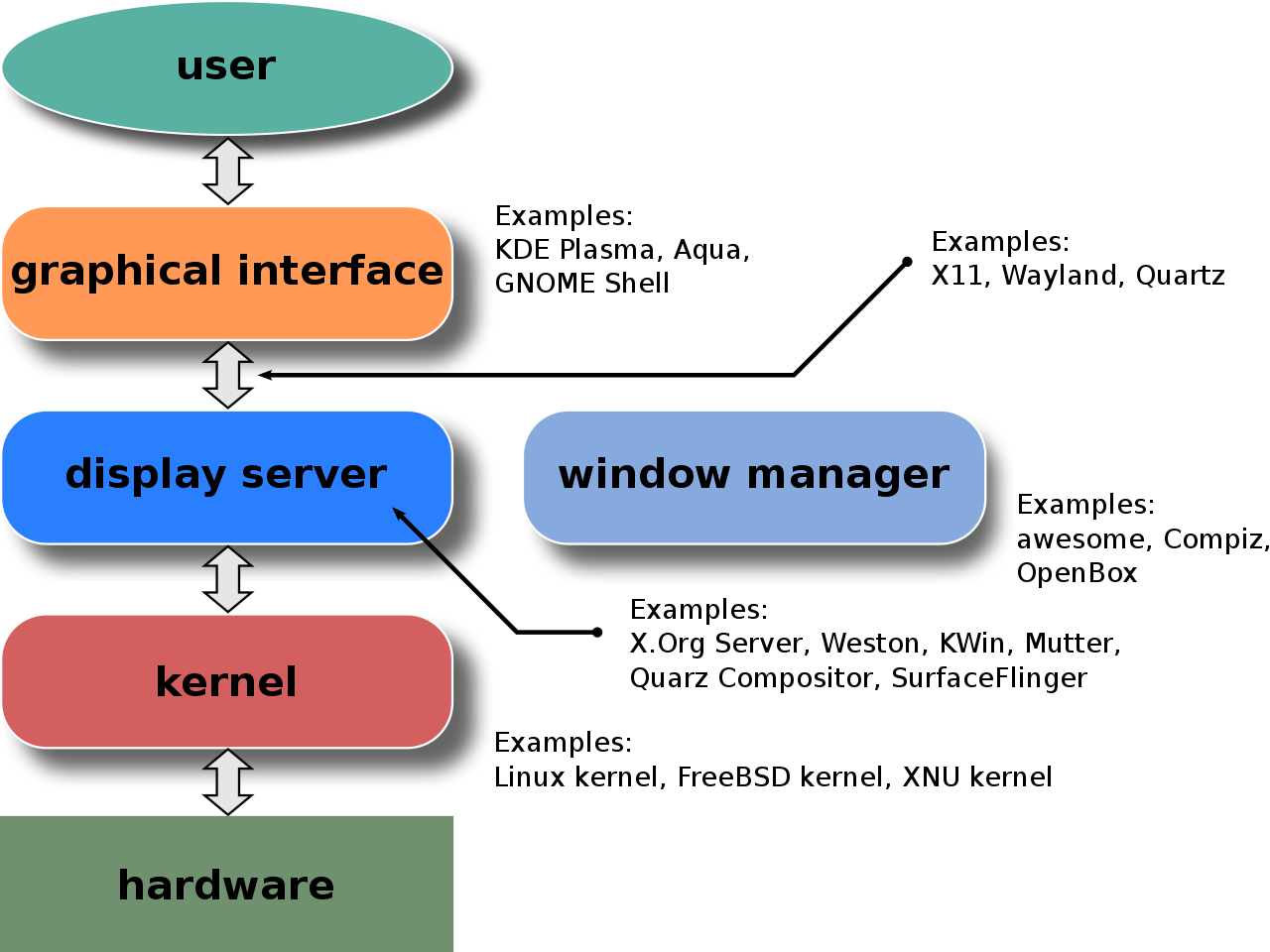
Linux GUI
A Linux distribution contains a display server, a window manager (manage windows, panel, menus, dash interfaces and core applications), and a desktop environment (eg status bars, drag-and-drop capabilities, etc)
These 3 items are bundled together to make what is known as a GUI environment
Using Linux
Using Linux through a GUI environment is similar to Windows or MacOSX
Linux users do not install software the same way that Windows users do: Linux has a tool known as a package manager
A package manager provides a way to search for software, install software, keep the software up to date and remove the software
Similar to Google or Apple store
Linux CLUI
Using Linux with GUI, it's already great ! Using CLUI = unlock the power of Linux !
Each Linux system contains a terminal
A terminal is where you enter Linux commands
It's called the Command Line User Interface
CLUI is one of the many strengths of Linux and can be more efficient than using the GUI
Linux CLUI
- CLUI allows users to be independent of distros (or UNIX systems like OSX)
- CLUI saves system resources which are consumed by GUIs
- CLUI allows users to easily work at distance (SSH)
- CLUI allows developers to join together simple (and less simple) commands to do complex things and automate... whatever you want to
People tend to think command line is difficult. It's not.
Linux Shell
A shell is a program that takes commands from the keyboard and gives them to the operating system to perform
The main function is to interpret your commands = language
The bash shell is one of several shells available for Linux
Learning the shell:
"When you are a child you use a computer by looking at the pictures. When you grow up, you learn to read and write"
It's more or less like SMSing to your PC, telling it what to do
Linux Shell
Shells have some built-in commands
A shell also supports programming constructs, allowing complex commands to be built from smaller parts = scripts
Scripts can be saved as files to become new commands
many commands on a typical Linux system are scripts
An open terminal show you a PROMPT waiting for your commands
Commands can have options and parameters
All your commands are saved in a history
Linux Shell Demo
Rename many files at once ?
mmv '*.JPG' '#1.jpg'
Download a youtube video ?
youtube-dl https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G7KNmW9a75Y&ab_channel=MileyCyrusVEVO
Convert color pictures in BW at once ?
#!/bin/bash
for file in *.jpg
do
convert ${file} -colorspace Gray "${file%.*}_bw.jpg"
echo "${file}... converted"
done
What you'll learn
Navigating the File System
Get up and running with the CLUI by navigating directories and files
Viewing and Changing Files and Directories
Learn to manipulate directories and files from the CLUI
Configuring the Environment
Learn to configure the environment using the CLUI
Accessing Linux remotely
Learn to use SSH (basics)
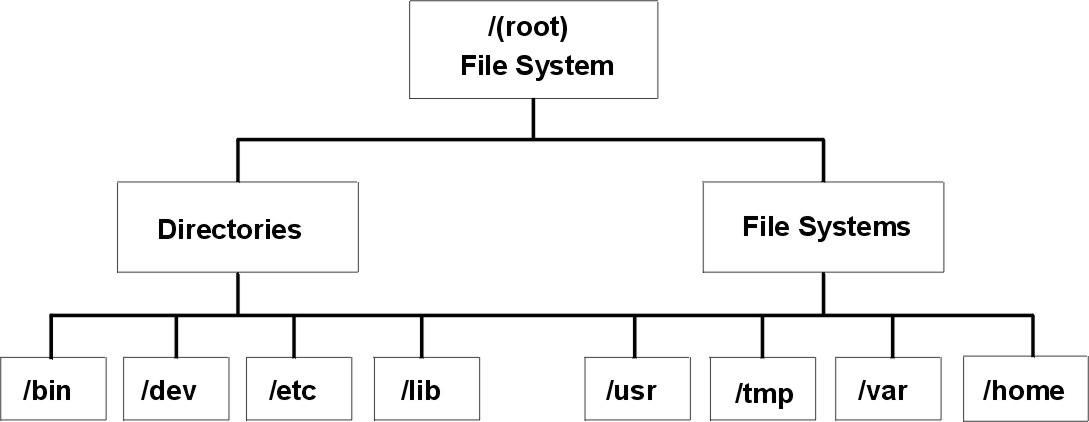
Navigating the File System
A file system is a section of hard disk that has been allocated to contain files
it's arranged like hierarchical tree structure
Files are grouped in the directory structure
The top of the tree is called root and / is used to present the root
Absolute paths
In the tree /users/usern/file1 is an absolute pathname
Relative paths
If you are already in the users directory, the relative pathname for file1 is usern/file1
~(tilda) points to the user's home directory. Useful if you are logging into a workstation with many users. It's the default working directory when you log in. If you are userusern, then/users/usern/file1is the same as~/file1.refers to the current directory..refers to the parent directory
Basic commands
ls: lists folders/files in a directorycd: change directory > usecd nameto navigate to directory namepwd: print working directory. Prints the path of the current directorydu: disk usage. Shows the disk usage of the current directoryman: manual
> useman nameto bring up a manual entry for command or program calledname
Creation
mkdir: usemkdir nameto create a new directory namednamein the current directorycp: usecp file1 file2to createfile2which is a copy offile1> can also usecp -rto copy whole directoriesmv: move = same as copy, but deletes the original file
Deletion
rm: delete files ( cannot recover your files after removed them ! ) > can also userm -rfto remove whole directories
Be careful : there is no trash in CLUI
tabis used for auto-complete > If a file/directory name was partly typed in, tab will auto-complete it
> If a file/directory name was partly typed in, tab will auto-complete it
If there are multiple options, tab will auto-complete up to the point where the options branch and show you a list of possible options
*is used as a wild card >rm blah*removes all files which start withblah: egblah1,blah2, andblahblahwould all be removed
using
cp public/* private/copies all files in apublicdirectory into aprivatedirectory, and keeps all file names intact
File permissions
Groups
Each file and directory has three user based permission groups
- owner :the
ownerpermissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users - group : the
grouppermissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users - all users : the
all userspermissions apply to all other users on the system, this is the permission group that you want to watch the most
Types
Each file or directory has three basic permission types
- read : the
readpermission refers to a user's capability to read the contents of the file - write : the
writepermission refer to a user's capability to write or modify a file or directory - execute : the
executepermission affects a user's capability to execute a file or view the contents of a directory
The following command :
ls -l
gives :
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
-rwxr-xr-x |
1 |
dupont |
grpelic |
3528 |
2022-08-04 |
file_1 |
drwxr-xr-x |
3 |
dupont |
grpelic |
512 |
2022-01-02 |
dir_1 |
lrwxr-xr-x |
2 |
dupont |
grpelic |
210 |
2020-12-16 |
short -> /data |
-rw------- |
1 |
dupont |
grpelic |
4587 |
2022-12-04 |
file_2 |
Linux privileges
Linux has a robust permissions system: this is a very good thing, as it enables a clear separation of roles among users
Especially between the root user and your standard user
Sometimes, though, you might want your standard user to have some or all of root's privileges : this is accomplished with sudo
Shell syntax rules
Shells use three "standard I/O streams"
stdinis the standard input stream, which provides input to commands.stdoutis the standard output stream, which displays output from commands.stderris the standard error stream, which displays error output from commands.
Shell has several meta-characters and control operators
|,&,>,;, etc.
Environment
In a bash shell many things constitute your environment
- the form of your prompt
- your home directory and your working directory
- the name of your shell
- functions that you have defined
- etc.
Environment includes many variables that may have been set by bash or by you
Access the value of a variable by prefixing its name with
$
Environment variables
USER: the name of the logged-in userUID: the numeric user id of the logged-in userHOME: the user's home directory (similar to~)PWD: the current working directorySHELL: the name of the shell
Set a shell variable : typing a name followed immediately by an equal sign ( = )
if the variable exists, you will modify it to assign the new value
You can use special files to control bash variables : $HOME/.bashrc
Remote Linux Access
SSH (or Secure SHell) is a protocol used to securely log onto remote systems
the most common way to access remote Linux and Unix-like servers
VNC (or Virtual Network Computing) is a software that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run
Aside from bandwidth, latency and security issues (which can vary a bit), the big differences are the functionality
- VNC exports a whole session, desktop and all (GUI)
- SSH runs a single program (CLUI) and show its windows on your machine
Remote Linux using SSH
You need:
- an access to the distant machine : login/password > or a login with SSH keys (with passphrase)
- the hostname or the IP address of the distant machine
- and (of course) a UNIX terminal
ssh -X pbarriat@coriolis.elic.ucl.ac.be
ssh -X -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.ceci pbarriat@gwcism.cism.ucl.ac.be
Remote Linux from Windows
Using a SSH client to reach a distant Linux Workstation
mobaXTerm is free and easy to use
allow you to test a Linux environmment but in CLUI only
Get a SSH client https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download-home-edition.html
How to use a SSH client https://support.ceci-hpc.be/doc/_contents/QuickStart/ConnectingToTheClusters/MobaXTerm.html
Scripting
How to do a backup ?
- with Dropbox or Google Drive ?
- with a private cloud such as Nextcloud ?
- with an other drive and/or an external drive ?
Backup on external drive ?
- manually ?
- with Windows tools ?
- with external softwares ?
Why don't do that with a simple linux script ?
Conclusions
| Advantages of Linux | Disadvantages of Linux |
|---|---|
| Cost | Not easy to master ( CLUI only ) |
| Security and robustness | Hardware compatibility issues ( sometimes ) |
| Freedom | Not compatible with some Windows software |
| Software | |
| Development |
Need to know more about available Linux applications ?
Check out the list of the best Linux software
Need help with bash scripting ?
Need help with Ubuntu ?
The massive community is one of Ubuntu's biggest strengths
Visit https://askubuntu.com/ or https://answers.launchpad.net/